- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Signal: AC / DC / Pulsed
Models (IPN / Output): 50A/4V · 200A/4V · 500A/4V
Measurement Range (IP): 0–100A · 0–400A · 0–1000A
Bandwidth (-3dB): DC–20kHz
Response Time: ≤5 μs
Accuracy (25°C): ≤±1%
Linearity: <1% FS
Supply: ±12–15V (±5%)
Consumption: <25 mA
Isolation: 2.5 kV / 50Hz / 1min (Primary–Secondary)
Operating Temp: -40 to +80°C
Load Resistance: ≥10 kΩ (25°C)
| Availability: | |
|---|---|
TR0214-LKH
TR
* Measures AC, DC and pulsed signals.
* Excellent accuracy, good linearity.
* Strong resistance to external interference, high common mode rejection ratio.
* Low temperature drift, low power consumption, wide frequency band.
* Split structure, easy to install.
* AC frequency conversion speed regulation.
* Servo motor traction.
* Uninterruptible power supply(UPS).
* Welding machine, battery power supply.
| Specification | 50A/4V | 200A/4V | 500A/4V | Unit | |
IPN | Primary Rated Input Current | 50 | 200 | 500 | A |
IP | Primary Current Measurement Range | 0-100 | 0-400 | 0-1000 | A |
VSN | Secondary rated output voltage | 4 | V | ||
VC | The Power Supply Voltage | ±12-15(±5%) | V | ||
IC | Current Consumption | <25 | mA | ||
Vd | Insulation Voltage | Between primary and secondary circuits:2.5kV/50Hz/1min | |||
εL | Linearity | <1 | %FS | ||
X | Precision | TA =25℃:≤±1 | % | ||
V0 | Offset Voltage | TA =25℃:≤±20 | mV | ||
VOM | Magnetic Offset Voltage | IP=0 after 3*IPN:≤±20 | mV | ||
VOT | Offset Voltage Temperature Drift | IP =0 TA =-40-+80℃:≤±1 | mV/℃ | ||
Tr | Response Time | ≤5 | μS | ||
f | Bandwidth(-3dB ) | DC-20 | KHz | ||
TA | Working Temperature | -40-+80 | ℃ | ||
TS | Storage Temperature | -45-+85 | ℃ | ||
RL | Load Resistance | TA =25℃:≥10 | kΩ | ||
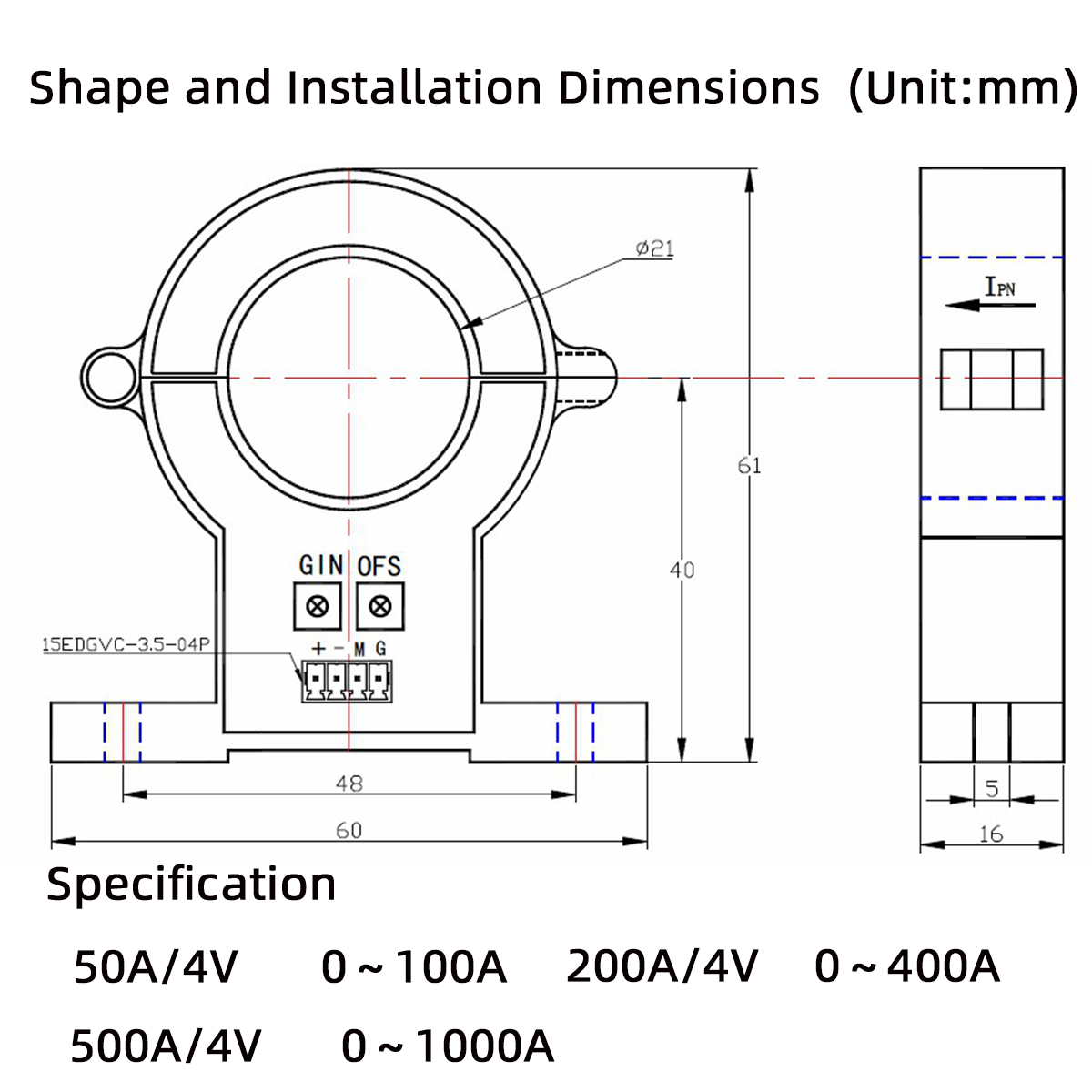
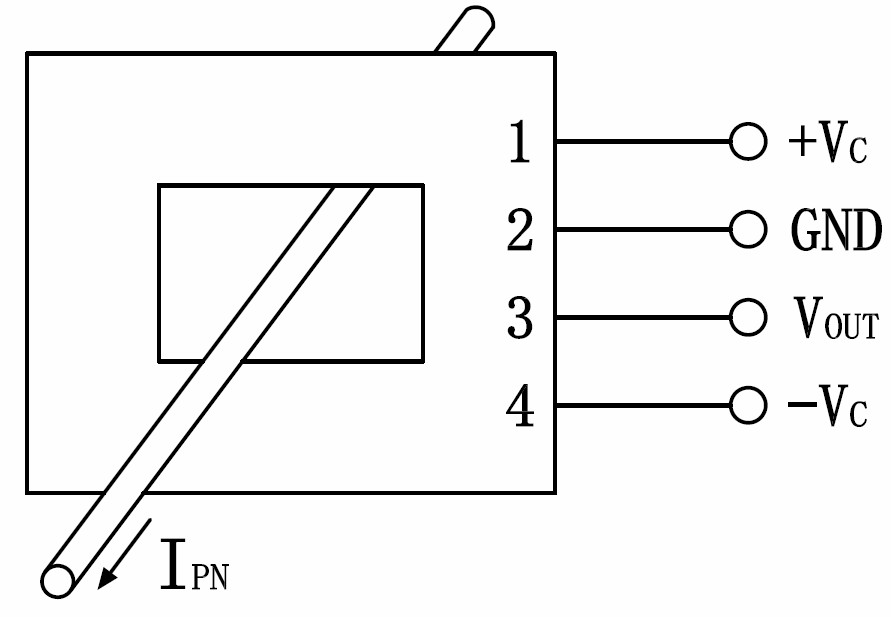
Notes:
IPN:Primary current input direction
+ :Positive 12V/15V power supply
- :Negative 12V/15V power supply M :Secondary signal output
G :Power ground OFS:Zero adjustment GIN:Amplitude adjustment
* The sensor should be wired correctly, otherwise it may damage the internal components of the sensor.
* Dynamic performance (di/dt and response time) is best when the input current row is fully filled with the primary perforation.
* Measures AC, DC and pulsed signals.
* Excellent accuracy, good linearity.
* Strong resistance to external interference, high common mode rejection ratio.
* Low temperature drift, low power consumption, wide frequency band.
* Split structure, easy to install.
* AC frequency conversion speed regulation.
* Servo motor traction.
* Uninterruptible power supply(UPS).
* Welding machine, battery power supply.
| Specification | 50A/4V | 200A/4V | 500A/4V | Unit | |
IPN | Primary Rated Input Current | 50 | 200 | 500 | A |
IP | Primary Current Measurement Range | 0-100 | 0-400 | 0-1000 | A |
VSN | Secondary rated output voltage | 4 | V | ||
VC | The Power Supply Voltage | ±12-15(±5%) | V | ||
IC | Current Consumption | <25 | mA | ||
Vd | Insulation Voltage | Between primary and secondary circuits:2.5kV/50Hz/1min | |||
εL | Linearity | <1 | %FS | ||
X | Precision | TA =25℃:≤±1 | % | ||
V0 | Offset Voltage | TA =25℃:≤±20 | mV | ||
VOM | Magnetic Offset Voltage | IP=0 after 3*IPN:≤±20 | mV | ||
VOT | Offset Voltage Temperature Drift | IP =0 TA =-40-+80℃:≤±1 | mV/℃ | ||
Tr | Response Time | ≤5 | μS | ||
f | Bandwidth(-3dB ) | DC-20 | KHz | ||
TA | Working Temperature | -40-+80 | ℃ | ||
TS | Storage Temperature | -45-+85 | ℃ | ||
RL | Load Resistance | TA =25℃:≥10 | kΩ | ||


Notes:
IPN:Primary current input direction
+ :Positive 12V/15V power supply
- :Negative 12V/15V power supply M :Secondary signal output
G :Power ground OFS:Zero adjustment GIN:Amplitude adjustment
* The sensor should be wired correctly, otherwise it may damage the internal components of the sensor.
* Dynamic performance (di/dt and response time) is best when the input current row is fully filled with the primary perforation.
Why Zero-Flux Leakage Current Sensors Are Ideal for Sensitive Leakage Monitoring Systems
Can An AC/DC Current Sensor Improve VFD Speed Control And Automated Systems?
How A Current Sensor Protects Transformer Grounding & Arrester Insulation
The Role of Hall Effect Current Sensors in Monitoring Railway Systems