- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-12-29 Origin: Site










Current sensors are devices used to measure the amount of electric current flowing through a conductor without significantly affecting the circuit operation. They play a critical role in power monitoring protection and control systems across industrial commercial and consumer applications. There are several main types of current sensors each based on a different working principle with distinct characteristics and application scenarios.
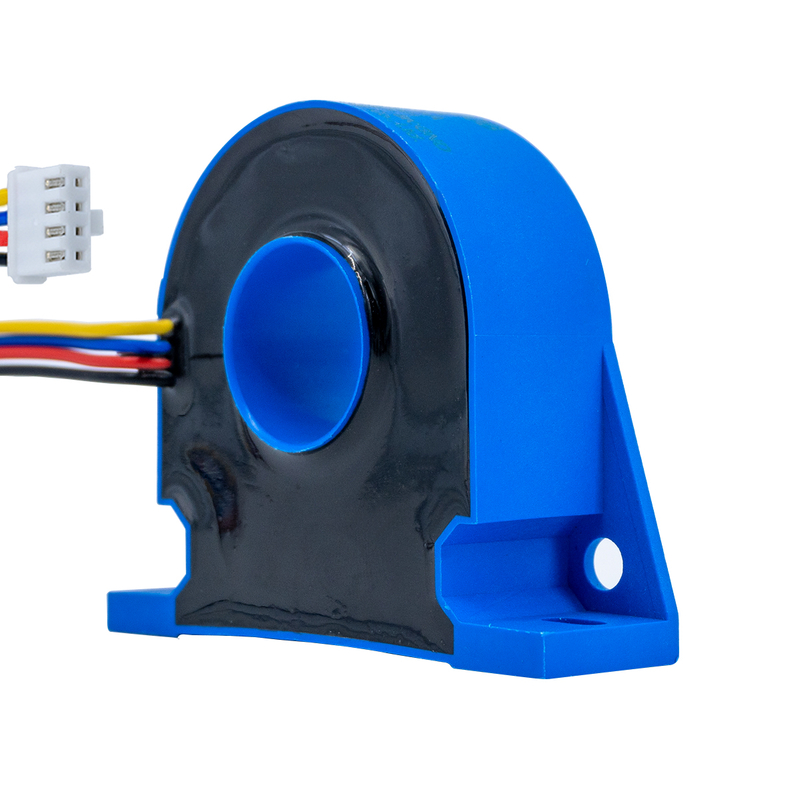

Current transformers are one of the most widely used types of current sensors for alternating current measurement. They operate on electromagnetic induction and provide an output current or voltage proportional to the primary current. Current transformers are known for high accuracy good linearity and electrical isolation between the primary and secondary circuits. They are commonly used in power distribution systems energy meters protective relays and industrial automation. Their limitation is that they are mainly suitable for AC measurement and cannot measure DC currents.
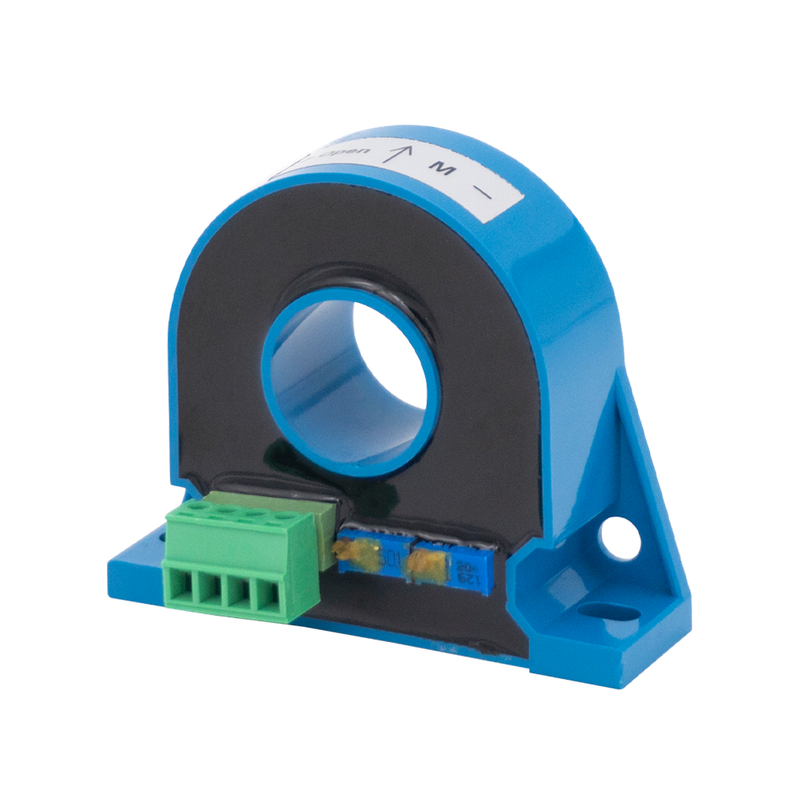
Hall effect current sensors are based on the Hall effect principle where a magnetic field generated by current flow is converted into a voltage signal. These sensors can measure both AC and DC currents which makes them highly versatile. Key features include wide current measurement range good electrical isolation and fast response time. Hall effect sensors are widely applied in motor drives inverters uninterruptible power supplies electric vehicles and renewable energy systems such as solar and wind power installations.
Rogowski coils are flexible air core current sensors designed for measuring alternating current especially at high current levels. Because they do not use a magnetic core they are immune to core saturation and offer excellent linearity over a wide current range. Rogowski coils are lightweight easy to install around large conductors and suitable for measuring transient and pulsed currents. They are commonly used in power quality monitoring fault detection and high current industrial applications. However they require signal integration circuitry and are not suitable for DC measurement.
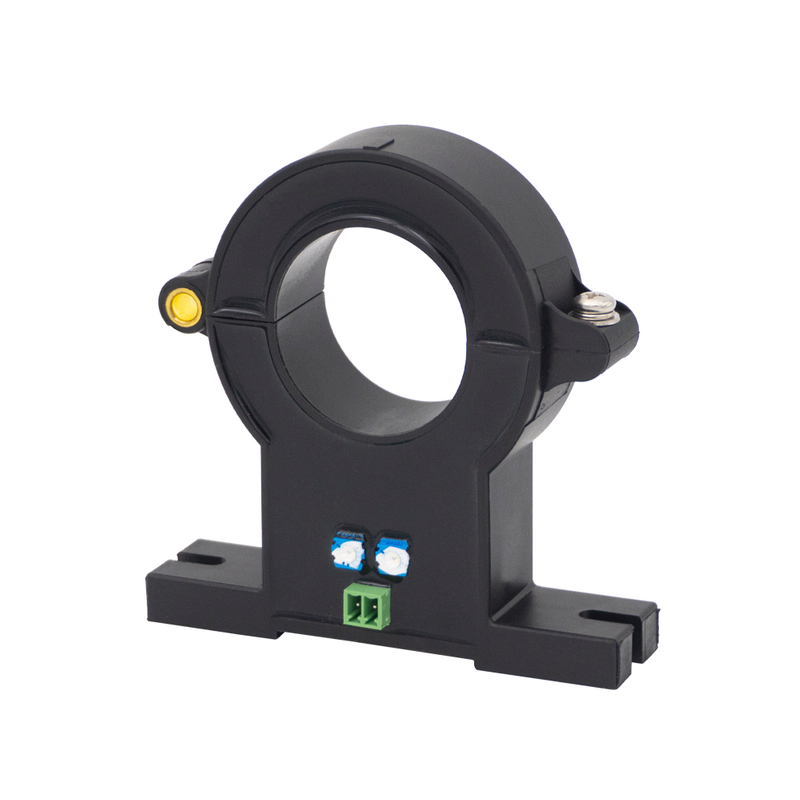

Fluxgate current sensors use a magnetic core driven into saturation to detect magnetic field changes caused by current flow. They offer extremely high accuracy low offset and excellent long term stability. Fluxgate sensors can measure both AC and DC currents with high precision making them suitable for applications such as precision power measurement medical equipment and calibration systems. Their disadvantages include higher cost larger size and more complex circuitry compared to Hall effect sensors.
In summary different types of current sensors are selected based on measurement requirements such as current type accuracy isolation response speed and environmental conditions. From simple shunt resistors to advanced fluxgate sensors each type plays a vital role in modern electrical and electronic systems supporting safe efficient and reliable operation across a wide range of applications.