- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
| Availability: | |
|---|---|
TR2215C-LBC
TR
A Current Sensor is a device that accurately measures AC or DC current flowing through a conductor and converts it into a standardized output signal, such as 4–20 mA, 0–10 V, or digital signals, for monitoring, control, and protection purposes. It provides high accuracy, fast response, electrical isolation, and reliable performance, ensuring precise and interference-free measurement in various environments. Current sensors are widely used in industrial automation, energy management, motor control, power distribution systems, renewable energy applications, and smart grids. By delivering real-time current data to control systems such as PLCs, SCADA, or DCS, they enable fault detection, load monitoring, energy optimization, and preventive maintenance, enhancing operational safety and efficiency. Compact, robust, and easy to integrate, current sensors play a critical role in improving system reliability, performance, and intelligent monitoring in modern electrical and industrial applications.
Small current measurement performance is stable
Excellent accuracy, good linearity
Wide measuring range and strong overload capacity
Perforated structure, no insertion loss
The signal system
Line detection
Leakage Monitoring System
Current difference measurement
Application examples
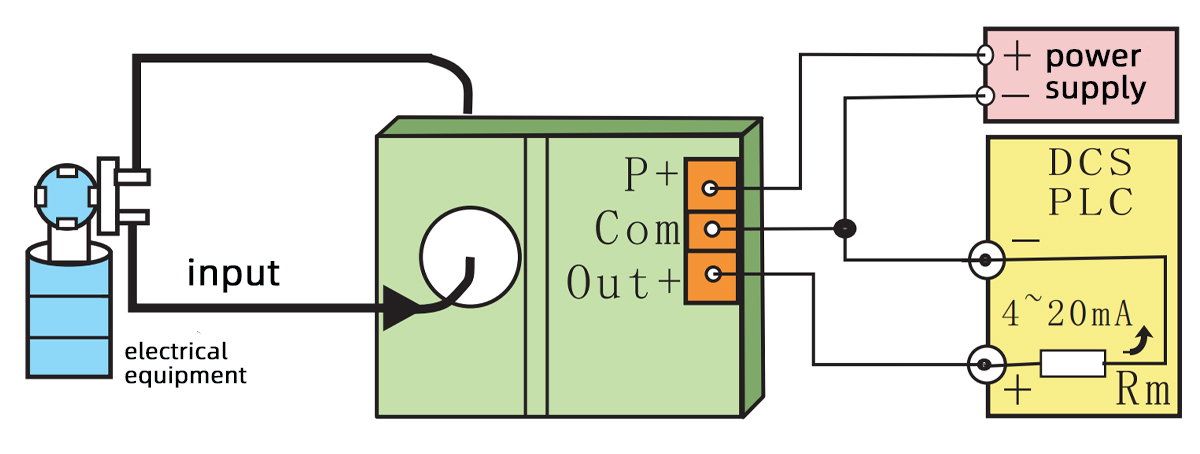
Example 1
Universal two isolation common ground output (one in, one out) is often used in this situation, where the power supply of the signal acquisition device is the same as that of the current transmitter, or the power supply of the current transmitter is directly provided by the signal acquisition device.
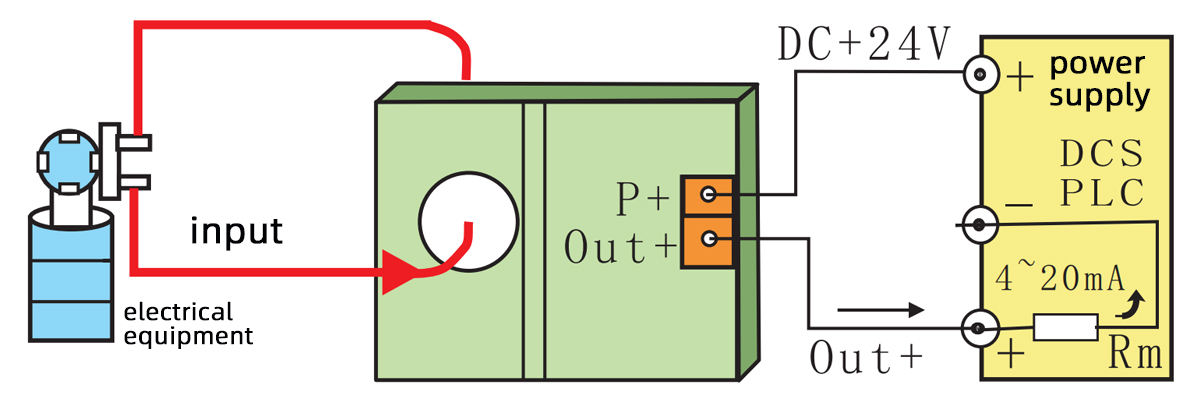
Example 2
The two-wire output (DC4~20mA) only requires 2 wires for output and power supply, which can save 1 wire compared to a general transmitter, reduce wire costs, and improve the reliability of the transmitter.
A Current Sensor is a device that accurately measures AC or DC current flowing through a conductor and converts it into a standardized output signal, such as 4–20 mA, 0–10 V, or digital signals, for monitoring, control, and protection purposes. It provides high accuracy, fast response, electrical isolation, and reliable performance, ensuring precise and interference-free measurement in various environments. Current sensors are widely used in industrial automation, energy management, motor control, power distribution systems, renewable energy applications, and smart grids. By delivering real-time current data to control systems such as PLCs, SCADA, or DCS, they enable fault detection, load monitoring, energy optimization, and preventive maintenance, enhancing operational safety and efficiency. Compact, robust, and easy to integrate, current sensors play a critical role in improving system reliability, performance, and intelligent monitoring in modern electrical and industrial applications.
Small current measurement performance is stable
Excellent accuracy, good linearity
Wide measuring range and strong overload capacity
Perforated structure, no insertion loss
The signal system
Line detection
Leakage Monitoring System
Current difference measurement
Application examples

Example 1
Universal two isolation common ground output (one in, one out) is often used in this situation, where the power supply of the signal acquisition device is the same as that of the current transmitter, or the power supply of the current transmitter is directly provided by the signal acquisition device.

Example 2
The two-wire output (DC4~20mA) only requires 2 wires for output and power supply, which can save 1 wire compared to a general transmitter, reduce wire costs, and improve the reliability of the transmitter.
Installation method: Fixed with flat screws
Primary rated current: 0.5A, 1A, 5A, 10A, 20A, 50A, 100A, 200A, 300A
Rated output: 1V, 2V, 5V, 10V, DC0-20mA, DC4-20mA, two-wire output, RS485
Auxiliary power supply: DC+24V; DC+15V,DC+12V;DC+5V;DC±12V; DC±15V; DC48V
Load capacity: Voltage output -5mA; Current output -6V
Accuracy: 0.1%; 0.2%; 0.5%
Overload capacity: 10 times nominal input
Isolation withstand voltage: 3KV/50Hz, 2mA, 1Min
Unbalanced voltage: ≤ 10mV
Temperature drift: ≤ 100PPM/° C
Linearity: 0.1%
Band width: 20~5KHz
Consumption current:<5mA+output current
Response time: Follow output<1mS, DC transmission output<250mS
Working temperature: -20 ° C~+80 ° C
Storage temperature: -25 ° C~+85 ° C
Can be made according to user requirements
Shape and Installation Dimension


Terminal output
Analog output
1: Positive power supply
2: Negative power supply (empty)
3: Output positive
4: Public's
*When outputting binary, pins 2 and 4 are empty
Rs485 output
1: Power supply positive
2:OUT+(A)
3:OUT -(B)
4: Negative power supply
Lead output
Analog output
Red: Positive power supply
Black: Negative power supply (empty)
Yellow: Output positive
Green: Public
*Black and green are empty when outputting in a two-wire system
Rs485 output
Red: Power supply positive
Black:OUT+(A)
Yellow:OUT -(B)
Green: Negative power suppl
Installation method: Fixed with flat screws
Primary rated current: 0.5A, 1A, 5A, 10A, 20A, 50A, 100A, 200A, 300A
Rated output: 1V, 2V, 5V, 10V, DC0-20mA, DC4-20mA, two-wire output, RS485
Auxiliary power supply: DC+24V; DC+15V,DC+12V;DC+5V;DC±12V; DC±15V; DC48V
Load capacity: Voltage output -5mA; Current output -6V
Accuracy: 0.1%; 0.2%; 0.5%
Overload capacity: 10 times nominal input
Isolation withstand voltage: 3KV/50Hz, 2mA, 1Min
Unbalanced voltage: ≤ 10mV
Temperature drift: ≤ 100PPM/° C
Linearity: 0.1%
Band width: 20~5KHz
Consumption current:<5mA+output current
Response time: Follow output<1mS, DC transmission output<250mS
Working temperature: -20 ° C~+80 ° C
Storage temperature: -25 ° C~+85 ° C
Can be made according to user requirements
Shape and Installation Dimension


Terminal output
Analog output
1: Positive power supply
2: Negative power supply (empty)
3: Output positive
4: Public's
*When outputting binary, pins 2 and 4 are empty
Rs485 output
1: Power supply positive
2:OUT+(A)
3:OUT -(B)
4: Negative power supply
Lead output
Analog output
Red: Positive power supply
Black: Negative power supply (empty)
Yellow: Output positive
Green: Public
*Black and green are empty when outputting in a two-wire system
Rs485 output
Red: Power supply positive
Black:OUT+(A)
Yellow:OUT -(B)
Green: Negative power suppl